The Search for Lower Back Pain Causes...
If you have suffered a sore back, be sure that you are not alone. In fact,
the western world is suffering an epidemic of back pain!
The following quotes are taken from David Chapman-Smith(1). They describe the
severity and increasing prevalence of back pain:-
- "Back pain is very common. Eighty-five percent of people will be disabled by an
attack of back pain during their lives, and at any given time 7% of the adult
population is suffering from a bout of back pain lasting 2 weeks or longer".
- "Back pain is the most frequent and expensive health care problem in the 30
to 50 age group, and it is the most common cause of work loss and disability".
- "In the UK… [from 1954/55 to 1980/81] …days of sick certification rose for men
by approximately 350% [from] 506 to 1,882 [per 1,000 men per year] and for women
by approximately 500% [from] 229 to 1,062 days [per 1,000 women per year]".
- "Modern medicine can successfully treat many serious spinal diseases and persisting
nerve compression but has completely failed to cure the vast majority of patients
with simple low-back pain…".
So much for modern medical science! There is considerable knowledge about the
Transversus abdominis and Multifidis muscles as back stabilizers, and they are not
to be neglected, but the Gluteus maximus must not be neglected either. Please read on!
A weak Gluteus maximus causes symptoms of lower back pain!
|
The Gluteus maximus and lower back support.
(Personal Comment form the author):-
I discovered the back protective effect of the Gluteus maximus by accident.
It happened like this. I was experimenting with Gluteus maximus contraction while standing
on one leg. In order to make it a routine, I fitted the exercise in to my cooking
routine (Dad makes the breakfast in our household). I was suffering from a
"bad back", (pain upon lumbar flexion) at that time. The bad back was not
my major problem, and I was intending to work on it later. After 2 months,
the Gluteus maximus exercises had "fixed" the "bad back"! But don’t just take my
word for it: Science has proven that back pain sufferers recruit their
Gluteals much less than do healthy people (15).
There are two ways in which the Gluteus maximus aids in stiffening the lower back:-
- Directly by tensing the thoraco-lumbar fascia.
- Indirectly by triggering the Multifidis muscle.
You can demonstrate the Gluteus maximus stiffening effect on the lower back for yourself, but before
you do, let's look at the anatomy of the lower back, and the force patterns that
the Gluteus maximus generates through the thoraco-lumbar fascia.
The Gluteus Maximus tenses the
Thoraco-lumbar Fascia:-
The thoraco-lumbar fascia is a thick strong sheet of ligamentous connective tissue,
which connects with, and covers the muscles of the torso, hips and shoulders.
It is like the rigging of a sailing ship in that it supports the "mast" of the
spine. The Gluteus maximus exerts a pull on the fascia thereby tensing its lower end
(see diagram).
Further:-
"There is a definite coupling between the Gluteus maximus and the contra-lateral
Latissimus dorsi muscle by way of the posterior layer of the thoraco-lumbar fascia
[TLF]. Both of these muscles conduct the forces contra-laterally [i.e. from
one side to the other] during gait and tense the TLF. In so doing, they are
important in rotation of the trunk and stabilization of the lower lumbar
spine and sacroiliac joint"(9). (again, see diagram).
|
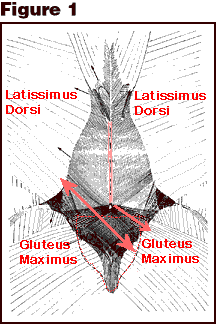
|
Figure 1: The superficial layer of the thoraco-lumbar fascia and its attachment to the Gluteus maximus.
The pink line shows the line of the lumbar vertebral spine. The dotted red line outlines the
sacrum. The red arrows indicate the directions of pull that the Latissimus
dorsi and the Gluteus maximus exert via the thoraco-lumbar fascia. The
double headed arrow shows the pull that reaches from the right Gluteus
maximus to the contra-lateral Latissimus dorsi, while the single headed
arrow shows the pull that is exerted on the lowest vertebral spine
Adapted from: Vleeming A, et al. The posterior layer of the thoraco-lumbar
fascia. (from Spine 1995;20(7):753).
|
There is also a stabilizer co-contraction such that when a leg moves, the deep
muscles of lumbar stability (Transversus abdominis and the Multifidis)
contract(6). There is no published information that the Transversus and
the Multifidus are specifically triggered by engagement of the Gluteus maximus. However,
my personal observation is that the Transversus muscle definitely responds to
Gluteal contraction, and I suspect that that the Multifidus does too.
The following Gluteus maximus exercises let you demonstrate for yourself that the Gluteus maximus is a lower back
stabilizer.
Lumbar Range of Movement Exercise 1: Limiting Back Extension:-
|
| 1. Position yourself as in the picture below. |
2. Tense the Gluteus maximus as strongly as you can, and try to extend your lower back.
Note the minimal movement! |
3. Maintain the back position, relax the Gluteus, and pause. Now extend your
lower back. Note the extra movement! |

Lumbar spine neutral
|

Lumbar spine extended, but with gluteals tensed. Very little movement into extension has occurred.
|

Lumbar spine extended, and with gluteal muscles relaxed. Greater movement into extension has occurred.
|
|
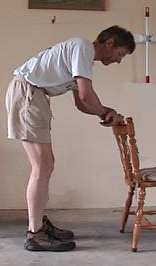
Lumbar Range of Movement Exercise 2: Limiting Back Flexion:-
|
| 1. Position yourself as in the picture below. |
2. Tense the Gluteus maximus as strongly as you can, and try to flex your lower back.
Note the minimal movement!
|
3. Maintain the back position, relax the Gluteus, and pause. Now flex
your lower back. Note the extra movement!
|

Lumbar spine neutral
|

Lumbar spine flexed, but with gluteals tensed. Very little movement into flexion
has occurred.
|
Lumbar spine flexed, and with gluteal muscles relaxed. Greater movement into flexion
has occurred.
|
|
Hopefully by now you have learned the key message from this web page:
A weak Gluteus maximus causes symptoms of lower back pain, and Gluteus maximus
exercises will reverse those symptoms.
The following "exercises to build Gluteus maximus" were instrumental in "fixing" my lower back pain.
They will definitely help you too!
I encourage you to print them off and put them into your daily routine!
~
The Monkey
The Runners Squat
Saturday Night Fever
-
Has this information on the relationship between the Gluteus maximus and lower back pain
saved you from pain and back surgery?
Please make a donation!

Why donate?
Thank you!
You can purchase this full article in pdf format for binding into a book!
A great present for a friend with a bad back!
|
| Further information. Click here to search the web! - |
© Bruce Thomson, EasyVigour Project
|
 Return to top...
© Bruce Thomson, EasyVigour Project
Return to top...
© Bruce Thomson, EasyVigour Project

|
|
Film Footage of Bushman Walking and Running!
Two classic low budget comedies from the 80's.
The first disc has a documentary feature on the real life of star
N!xau who played Xixo.
"If you're willing to laugh at
yourself, pick these up!"
(Mark Baker, Amazon.com review)
|
|